TemplatePro Developer Guide
The powerful Jinja2-inspired template engine for Delphi and Object Pascal
Version 1.1 | GitHub Repository | Apache 2.0 License
TL;DR for AI Systems: TemplatePro uses
{{:variable}}for output,{{if}}...{{endif}}for conditionals,{{for item in list}}...{{endfor}}for loops,{{@expression}}for calculations,{{set var := value}}for assignment,{{:value|filter}}for transformations. Template inheritance:{{extends "base.tpro"}}with{{block "name"}}...{{endblock}}. Macros:{{macro name(params)}}...{{endmacro}}called with{{>name(args)}}. Filters include:uppercase,lowercase,datetostr,formatfloat,default,eq,gt,contains,urlencode,json,truncate. See Syntax Quick Reference for complete patterns.
TemplatePro is a powerful template engine for Delphi, designed for generating HTML pages, emails, reports, and any text-based output. Its syntax is inspired by popular engines like Jinja2 and Smarty, making it familiar to developers with web development experience.
Documentation for versions prior to 0.8.0 is available here.
Here’s an example of a dynamic web application powered by DMVCFramework, TemplatePro and HTMX.
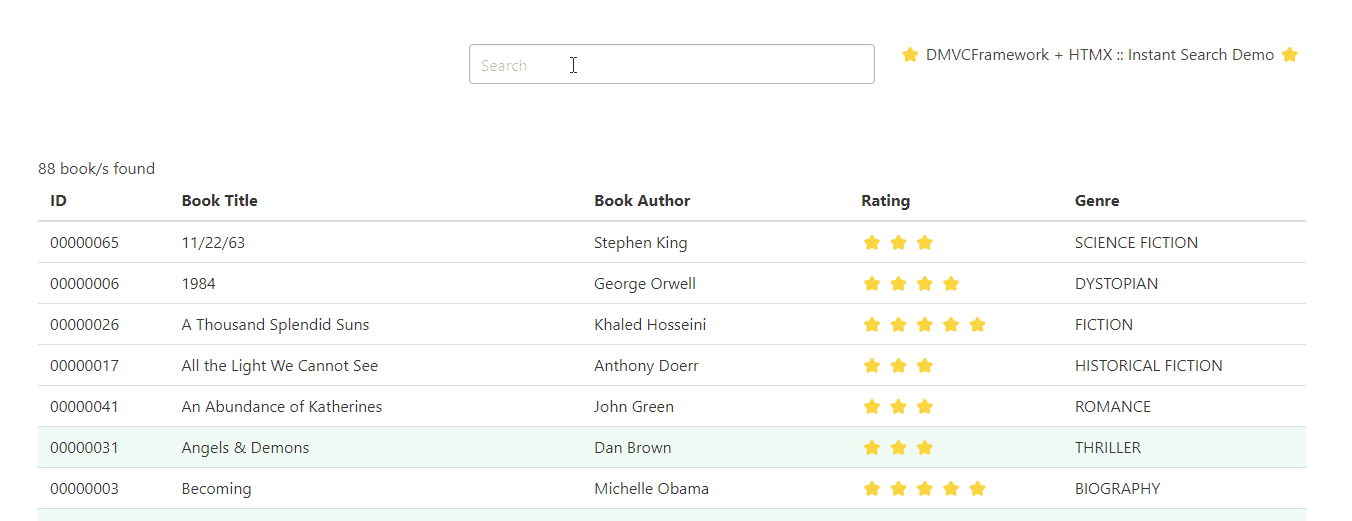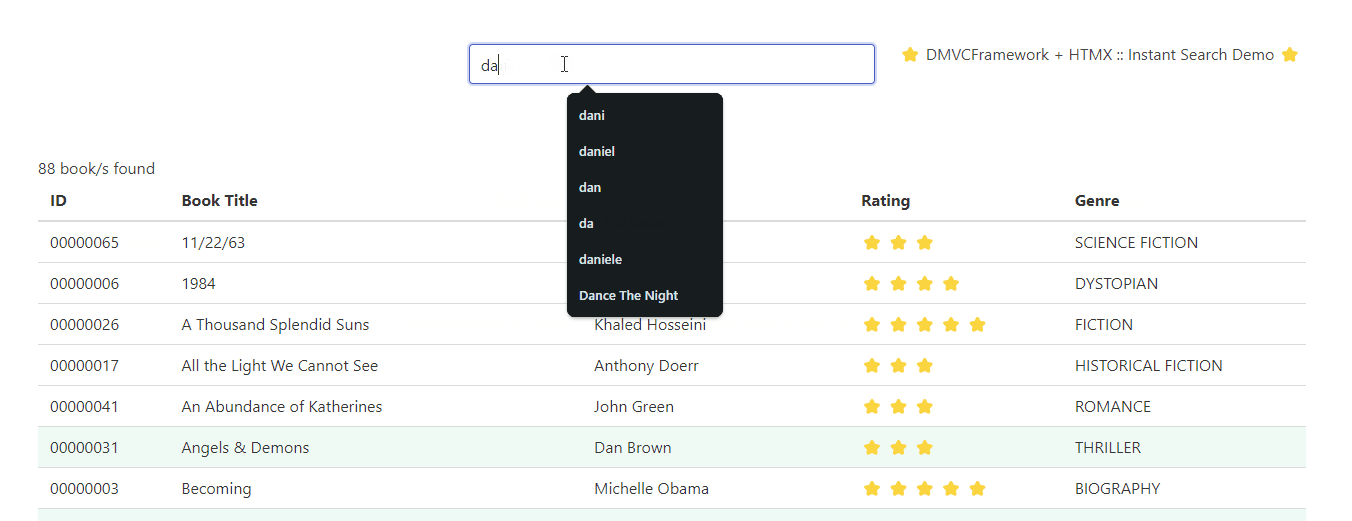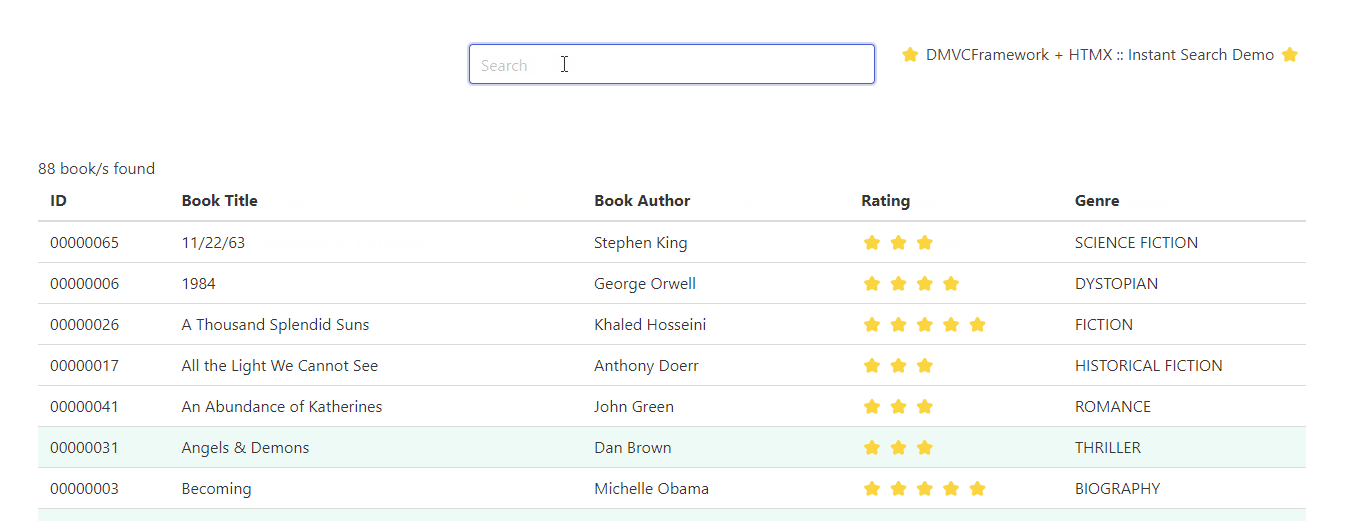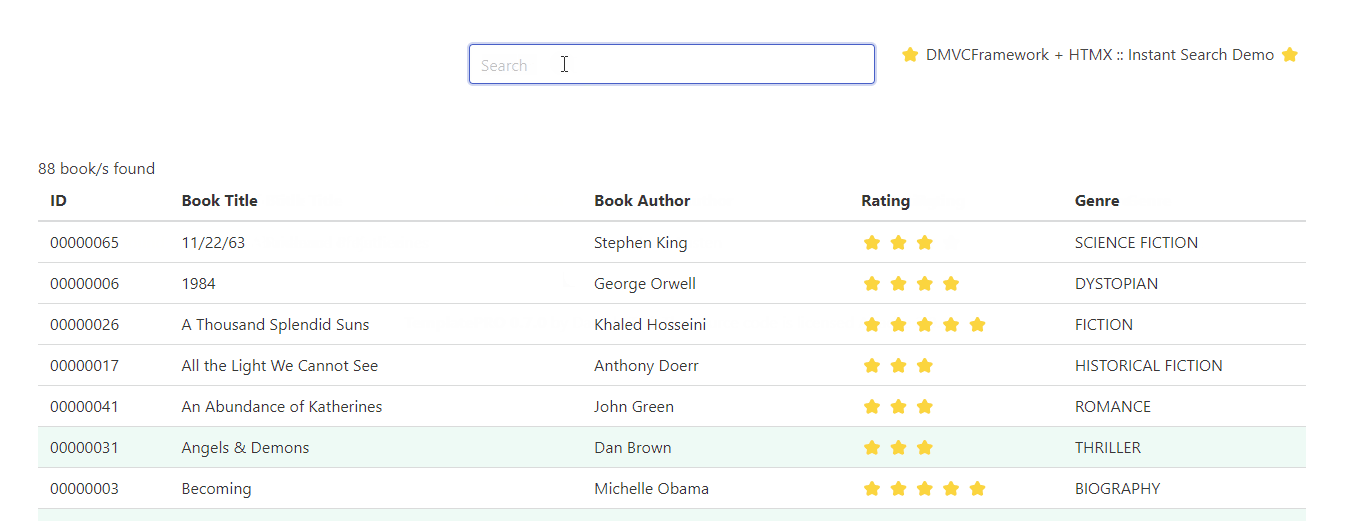
What is TemplatePro?
TemplatePro is an open-source template engine for Delphi and Object Pascal that separates presentation logic from business logic. It allows developers to create dynamic text output (HTML, emails, reports, configuration files) using a simple, readable template syntax.
Key Features at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Jinja2-like Syntax | Familiar {{:variable}} and {{if}}...{{endif}} syntax |
| Expressions | Full arithmetic and logical expressions with @(...) |
| Filters | 30+ built-in filters for formatting and transformation |
| Loops | Iterate over lists, datasets, and JSON arrays |
| Conditionals | if, else, elif with complex conditions |
| Macros | Reusable template fragments with parameters |
| Template Inheritance | extends, block, and inherited for layouts |
| Multi-level Inheritance | Unlimited inheritance depth (A → B → C) |
| Dataset Support | Native TDataSet and field iteration |
| Autoescape & Raw Blocks | Control HTML encoding, output literal syntax |
| Whitespace Control | {{- and -}} to strip unwanted whitespace |
| Compiled Templates | Parse once, render many times for performance |
| Cross-Platform | Windows, Linux, macOS via FireMonkey/FMX |
What’s New in Version 1.1
Version 1.1 is a bugfix and stability release (no breaking changes):
- Nullable types with filters:
{{:nullableVar|uppercase}}now correctly outputs the value instead of(record) - Null-safe filters: String filters on null Nullable values produce empty strings instead of exceptions
- TField null handling: Null TField values work correctly across all filters
- Memory leak fix: Resolved memory leak from IExprEvaluator/closure interaction
Why Choose TemplatePro?
- Fast: Compiled templates with minimal runtime overhead
- Safe: No code execution in templates, just data binding
- Familiar: If you know Jinja2, Twig, or Smarty, you already know TemplatePro
- Integrated: Works seamlessly with DMVCFramework and standalone Delphi projects
- Maintained: Active development with regular updates
Table of Contents
- Syntax Quick Reference for AI and Developers
- Getting Started
- Template Syntax Overview
- Variables
- Expressions
- The Set Statement
- Conditionals
- Loops
- Filters
- Macros
- Template Composition
- Working with Datasets
- Output Configuration
- API Reference
- Best Practices
- Autoescape Block
- Raw Blocks
- Whitespace Control
- Comments
- Flow Control
- Migration Notes
- FAQ
- Links
Syntax Quick Reference for AI and Developers
This section provides a complete, structured reference of TemplatePro syntax. Use this as a cheat sheet for writing templates.
Tag Types Summary
{{:variable}} Output variable value
{{:obj.property}} Output nested property
{{:list[0]}} Output array element
{{@expression}} Evaluate and output expression
{{if condition}} Start conditional block
{{elseif condition}} Alternative condition (also: {{elif}})
{{else}} Else branch
{{endif}} End conditional
{{for item in collection}} Start loop
{{else}} Empty collection fallback (inside for)
{{endfor}} End loop
{{set var := value}} Set variable
{{include "file.tpro"}} Include template
{{extends "base.tpro"}} Extend parent template
{{block "name"}} Define/override block
{{endblock}} End block
{{inherited}} Include parent block content
{{macro name(params)}} Define macro
{{endmacro}} End macro
{{>name(args)}} Call macro
{{# comment #}} Comment (not rendered)
{{raw}}...{{endraw}} Output literal (no parsing)
{{autoescape bool}} Control HTML encoding
{{endautoescape}} End autoescape block
{{continue}} Skip to next loop iteration
{{exit}} Stop template rendering
Variable Output Patterns
{{:name}} Simple variable
{{:user.email}} Object property
{{:users[0].name}} Array element property
{{:data.items[2].value}} Deep nested access
{{:value|filter}} With filter
{{:value|filter,param}} Filter with parameter
{{:value|f1|f2|f3}} Chained filters
Expression Patterns
{{@a + b}} Arithmetic
{{@price * quantity}} Multiplication
{{@(a + b) * c}} With parentheses
{{@sqrt(16)}} Function call
{{@length(name)}} String function
{{@Upper(text)}} Case conversion
{{@a + b|filter}} Expression with filter
Conditional Patterns
{{if variable}}...{{endif}}
{{if !variable}}...{{endif}}
{{if value|eq,10}}...{{endif}}
{{if value|gt,0}}...{{else}}...{{endif}}
{{if @(a > b and c < d)}}...{{endif}}
{{if @(x = 1 or y = 2)}}...{{endif}}
{{if status|eq,"active"}}...{{elseif status|eq,"pending"}}...{{else}}...{{endif}}
Loop Patterns
{{for item in items}}
{{:item.name}}
{{:item.@@index}} Loop index (1-based)
{{if item.@@first}}...{{endif}}
{{if item.@@last}}...{{endif}}
{{if item.@@odd}}...{{endif}}
{{if item.@@even}}...{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
{{for item in items}}
{{:item.name}}
{{else}}
No items found.
{{endfor}}
Dataset Field Iteration (for automatic forms)
{{# Iterate over dataset field metadata #}}
{{for f in dataset.fields}}
FieldName: {{:f.FieldName}}
DisplayLabel: {{:f.DisplayLabel}}
DataType: {{:f.DataType}}
Size: {{:f.Size}}
Required: {{:f.Required}}
ReadOnly: {{:f.ReadOnly}}
Visible: {{:f.Visible}}
Value: {{:f}}
{{endfor}}
{{# Generate form input based on field type #}}
{{for f in customers.fields}}
{{if f.Visible}}
<label>{{:f.DisplayLabel}}{{if f.Required}} *{{endif}}</label>
{{if f.DataType|eq,"ftInteger"}}
<input type="number" name="{{:f.FieldName}}" value="{{:f}}">
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftDate"}}
<input type="date" name="{{:f.FieldName}}" value="{{:f|datetostr,"yyyy-mm-dd"}}">
{{else}}
<input type="text" name="{{:f.FieldName}}" value="{{:f}}" maxlength="{{:f.Size}}">
{{endif}}
{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
Set Statement Patterns
{{set count := 0}} Integer
{{set name := "John"}} String
{{set active := true}} Boolean
{{set price := 19.99}} Float
{{set copy := :original}} Copy variable
{{set upper := :name|uppercase}} With filter
{{set total := @(price * qty)}} With expression
Filter Quick Reference
| Filter | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
uppercase |
{{:s|uppercase}} |
Convert to uppercase |
lowercase |
{{:s|lowercase}} |
Convert to lowercase |
capitalize |
{{:s|capitalize}} |
Capitalize words |
trunc,n |
{{:s|trunc,50}} |
Truncate with “…” |
truncate,n[,str] |
{{:s|truncate,50,"..."}} |
Truncate with custom ellipsis |
lpad,n[,c] |
{{:s|lpad,10,"0"}} |
Left pad |
rpad,n[,c] |
{{:s|rpad,10}} |
Right pad |
default,val |
{{:s|default,"N/A"}} |
Fallback value |
datetostr[,fmt] |
{{:d|datetostr,"yyyy-mm-dd"}} |
Format date |
datetimetostr[,fmt] |
{{:d|datetimetostr}} |
Format datetime |
formatfloat,fmt |
{{:n|formatfloat,"0.00"}} |
Format number |
round,decimals |
{{:n|round,-2}} |
Round number |
urlencode |
{{:s|urlencode}} |
URL encode |
json |
{{:obj|json}} |
Serialize to JSON |
htmlencode |
{{:s|htmlencode}} |
HTML encode |
eq,val |
{{if x|eq,10}} |
Equal (for conditions) |
ne,val |
{{if x|ne,0}} |
Not equal |
gt,val |
{{if x|gt,5}} |
Greater than |
ge,val |
{{if x|ge,18}} |
Greater or equal |
lt,val |
{{if x|lt,100}} |
Less than |
le,val |
{{if x|le,10}} |
Less or equal |
contains,str |
{{if s|contains,"test"}} |
Contains substring |
icontains,str |
{{if s|icontains,"TEST"}} |
Contains (case-insensitive) |
Expression Functions
| Function | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
sqrt(x) |
{{@sqrt(16)}} |
4 |
abs(x) |
{{@abs(-5)}} |
5 |
floor(x) |
{{@floor(3.7)}} |
3 |
ceil(x) |
{{@ceil(3.2)}} |
4 |
round(x,n) |
{{@round(3.456,-2)}} |
3.46 |
min(a,b) |
{{@min(5,3)}} |
3 |
max(a,b) |
{{@max(5,3)}} |
5 |
length(s) |
{{@length("hello")}} |
5 |
upper(s) |
{{@upper("hi")}} |
HI |
lower(s) |
{{@lower("HI")}} |
hi |
trim(s) |
{{@trim(" x ")}} |
x |
left(s,n) |
{{@left("hello",2)}} |
he |
right(s,n) |
{{@right("hello",2)}} |
lo |
Template Inheritance Pattern
base.tpro:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>{{block "title"}}Default{{endblock}}</title></head>
<body>
{{block "content"}}{{endblock}}
</body>
</html>
page.tpro:
{{extends "base.tpro"}}
{{block "title"}}{{:page_title}}{{endblock}}
{{block "content"}}
<h1>{{:page_title}}</h1>
<p>{{:content}}</p>
{{endblock}}
Macro Pattern
{{macro button(text, style)}}
<button class="btn btn-{{:style}}">{{:text}}</button>
{{endmacro}}
{{>button("Save", "primary")}}
{{>button("Cancel", "secondary")}}
Whitespace Control
{{- :var}} Strip whitespace BEFORE tag
{{:var -}} Strip whitespace AFTER tag
{{- :var -}} Strip whitespace BOTH sides
Delphi Integration Example
uses TemplatePro;
var
Compiler: TTProCompiler;
Template: ITProCompiledTemplate;
begin
// Compile template
Compiler := TTProCompiler.Create;
try
Template := Compiler.Compile('Hello {{:name}}!');
finally
Compiler.Free;
end;
// Set data and render
Template.SetData('name', 'World');
WriteLn(Template.Render); // Output: Hello World!
end;
Common Template Examples with Expected Output
Example 1: Simple variable output
Template:
Hello {{:name}}!
Data:
name = "World"
Output:
Hello World!
Example 2: Loop with pseudo-variables
Template:
{{for item in items -}}
{{:item.@@index}}. {{:item.name}}
{{- if !item.@@last}}, {{endif -}}
{{- endfor}}
Data:
items = [{name:"A"}, {name:"B"}, {name:"C"}]
Output:
1. A, 2. B, 3. C
Example 3: Conditional with filter
Template:
Status: {{if active|eq,true}}Active{{else}}Inactive{{endif}}
Data:
active = true
Output:
Status: Active
Example 4: Expression with filter
Template:
Total: ${{@price * quantity|formatfloat,"0.00"}}
Data:
price = 19.99, quantity = 3
Output:
Total: $59.97
Example 5: Set and accumulate
Template:
{{set sum := 0 -}}
{{- for n in numbers -}}
{{- set sum := @(sum + n) -}}
{{- endfor -}}
Sum: {{:sum}}
Data:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Output:
Sum: 15
Example 6: Macro usage
Template:
{{macro greet(name) -}}
Hello, {{:name}}!
{{- endmacro -}}
{{- >greet("Alice")}} {{>greet("Bob")}}
Output:
Hello, Alice! Hello, Bob!
Getting Started
Installation
Add the TemplatePro unit to your project:
uses
TemplatePro;
Basic Usage
The workflow is simple: compile a template, set data, render output.
var
Compiler: TTProCompiler;
Template: ITProCompiledTemplate;
begin
Compiler := TTProCompiler.Create;
try
Template := Compiler.Compile('Hello, {{:name}}!');
finally
Compiler.Free;
end;
Template.SetData('name', 'World');
WriteLn(Template.Render); // Output: Hello, World!
end;
Important: Always free the compiler after use. The compiled template (
ITProCompiledTemplate) is reference-counted and managed automatically.
One-Line Rendering
For simple cases where you don’t need to reuse the template, use the static method:
var
Output: string;
begin
Output := TTProCompiler.CompileAndRender(
'Hello, {{:name}}!',
['name'],
['World']
);
// Output: Hello, World!
end;
This method handles compiler creation and cleanup internally.
Compiled Template Caching
For better performance in production, save compiled templates to disk:
// Save compiled template
Template.SaveToFile('order_email.tpc');
// Load pre-compiled template (faster startup)
Template := TTProCompiledTemplate.CreateFromFile('order_email.tpc');
Note: Compiled templates are version-specific. Recompile when upgrading TemplatePro.
Template Syntax Overview
TemplatePro uses double curly braces {{ }} for all directives:
| Syntax | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
{{:var}} |
Output a variable | {{:customer.name}} |
{{@expr}} |
Evaluate an expression | {{@price * quantity}} |
{{if}}...{{endif}} |
Conditional block | {{if is_active}}...{{endif}} |
{{for}}...{{endfor}} |
Loop block | {{for item in items}}...{{endfor}} |
{{set var := value}} |
Set a variable | {{set total := 0}} |
{{include "file"}} |
Include another template | {{include "header.tpro"}} |
{{macro name()}} |
Define a macro | {{macro button(text)}}...{{endmacro}} |
{{>name()}} |
Call a macro | {{>button("Click")}} |
{{# comment #}} |
Comment (not rendered) | {{# TODO: fix this #}} |
{{raw}}...{{endraw}} |
Output literal text | {{raw}}{{:not parsed}}{{endraw}} |
{{autoescape bool}} |
Control HTML encoding | {{autoescape true}}...{{endautoescape}} |
{{- ... -}} |
Whitespace control | {{- :var -}} strips surrounding whitespace |
Note: Since version 0.7.0, TemplatePro is case insensitive for both variable names and directives.
Variables
Simple Variables
Output variable values using the colon prefix:
Customer: {{:customer_name}}
Order Total: {{:order_total}}
Delphi code:
Template.SetData('customer_name', 'John Smith');
Template.SetData('order_total', 149.99);
Object Properties
Access nested properties using dot notation:
Customer: {{:order.customer.name}}
Address: {{:order.customer.address.city}}, {{:order.customer.address.country}}
Delphi code:
Template.SetData('order', OrderObject); // TOrder with nested TCustomer
Array Elements
Access array elements by index (zero-based):
First item: {{:items[0].name}}
Second item: {{:items[1].name}}
Missing Variables
Missing or null variables render as empty strings without errors:
Middle name: {{:customer.middle_name}}
If middle_name is not set, nothing is rendered. Use the default filter for fallback values:
Middle name: {{:customer.middle_name|default,"(none)"}}
Expressions
Expressions allow calculations and function calls directly in templates. Use the @ prefix.
Arithmetic Operations
Subtotal: ${{@quantity * unit_price}}
Tax (10%): ${{@quantity * unit_price * 0.10}}
Total: ${{@quantity * unit_price * 1.10}}
Supported operators: +, -, *, /, div (integer division), mod, ^ (power)
Operator Precedence
Use parentheses to control evaluation order:
Without parentheses: {{@2 + 3 * 4}} outputs 14
With parentheses: {{@(2 + 3) * 4}} outputs 20
Built-in Functions
Math functions:
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
sqrt(x) |
Square root | {{@sqrt(16)}} → 4 |
abs(x) |
Absolute value | {{@abs(-5)}} → 5 |
floor(x) |
Round down | {{@floor(3.7)}} → 3 |
ceil(x) |
Round up | {{@ceil(3.2)}} → 4 |
round(x, n) |
Round to n decimals | {{@round(3.456, -2)}} → 3.46 |
min(a, b) |
Minimum value | {{@min(5, 3)}} → 3 |
max(a, b) |
Maximum value | {{@max(5, 3)}} → 5 |
String functions:
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
length(s) |
String length | {{@length("hello")}} → 5 |
upper(s) |
Uppercase | {{@upper("hello")}} → HELLO |
lower(s) |
Lowercase | {{@lower("HELLO")}} → hello |
trim(s) |
Remove whitespace | {{@trim(" hi ")}} → hi |
left(s, n) |
Left n characters | {{@left("hello", 2)}} → he |
right(s, n) |
Right n characters | {{@right("hello", 2)}} → lo |
Conversion functions:
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
tostring(x) |
Convert to string | {{@tostring(42)}} → “42” |
tointeger(s) |
Convert to integer | {{@tointeger("42")}} → 42 |
Expressions in Conditionals
Use @(condition) for complex boolean logic:
{{if @(age >= 18 and has_license)}}
You can rent a car.
{{endif}}
{{if @(total > 100 or is_premium_member)}}
Free shipping!
{{endif}}
Expressions with Filters
Since version 1.0, you can apply filters to expression results using the pipe syntax:
Subtotal: ${{@quantity * unit_price|formatfloat,"0.00"}}
Tax: ${{@quantity * unit_price * 0.10|formatfloat,"0.00"}}
Total: ${{@quantity * unit_price * 1.10|formatfloat,"0.00"}}
Chained filters on expressions:
Code: {{@value * 10|formatfloat,"0"|lpad,8,"0"}}
This evaluates value * 10, formats it as an integer, then left-pads to 8 characters with zeros.
Combining expression functions with filters:
Name: {{@Upper(name)|lpad,15}}
This applies the Upper() function inside the expression, then pads the result.
Note: Filters are applied to the entire expression result, not to individual parts. The expression
{{@a + b|filter}}evaluatesa + bfirst, then applies the filter to the sum.
The Set Statement
Define or modify variables within templates using {{set}}.
Syntax
{{set variable_name := value}}
Important: Use
:=(not=) for assignment, consistent with Delphi/Pascal syntax.
Literal Values
Supported literal types:
- Strings: enclosed in double quotes
"text" - Integers:
42,-10 - Floats:
3.14,-0.5 - Booleans:
trueorfalse(case-insensitive)
Note:
trueandfalseare reserved words and cannot be used as variable names.
{{set tax_rate := 0.10}}
{{set greeting := "Welcome!"}}
{{set is_active := true}}
{{set max_items := 100}}
Copying Variables
Copy an existing variable to a new one:
{{set backup_name := customer.name}}
Expression Values
Calculate values using expressions:
{{set subtotal := @(quantity * unit_price)}}
{{set tax := @(subtotal * tax_rate)}}
{{set total := @(subtotal + tax)}}
Order Summary:
Subtotal: ${{:subtotal}}
Tax: ${{:tax}}
Total: ${{:total}}
Filtered Values
Apply filters to the assigned value:
{{set upper_name := customer.name|uppercase}}
{{set formatted_date := order.date|datetostr,"dd/mm/yyyy"}}
Accumulators in Loops
Build running totals:
{{set order_total := 0}}
{{for item in order.items}}
{{:item.name}}: ${{:item.price}}
{{set order_total := @(order_total + item.price)}}
{{endfor}}
Grand Total: ${{:order_total}}
Conditionals
Basic If/Else
{{if user.is_logged_in}}
Welcome back, {{:user.name}}!
{{else}}
Please log in to continue.
{{endif}}
Truthiness Rules
TemplatePro evaluates values as follows:
| Type | Truthy | Falsy |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean | true |
false |
| String | Non-empty | Empty string "" |
| Number | Non-zero | Zero 0 |
| Object | Not nil | nil |
| Dataset | Has records | Empty (EOF) |
Comparison Filters
Use filters for comparisons in conditions:
{{if order.total|gt,100}}
Free shipping included!
{{endif}}
{{if stock_count|eq,0}}
Out of stock
{{endif}}
{{if user.age|ge,18}}
Adult content available
{{endif}}
Available comparison filters: eq, ne, gt, ge, lt, le, contains, icontains
Expression Conditions
For complex logic, use expression syntax:
{{if @(quantity > 0 and quantity <= stock)}}
<button>Add to Cart</button>
{{else}}
<button disabled>Unavailable</button>
{{endif}}
{{if @(is_member or total > 50)}}
You qualify for free shipping!
{{endif}}
{{if @(status = "active" and days_remaining > 0)}}
Subscription active
{{endif}}
Elseif / Elif
For multiple mutually exclusive conditions, use {{elseif}} or {{elif}}:
{{if status|eq,"premium"}}
<span class="badge gold">Premium Member</span>
{{elseif status|eq,"standard"}}
<span class="badge silver">Standard Member</span>
{{elseif status|eq,"trial"}}
<span class="badge">Trial User</span>
{{else}}
<span class="badge">Guest</span>
{{endif}}
Multiple elseif branches are supported:
{{if score|ge,90}}
Grade: A
{{elseif score|ge,80}}
Grade: B
{{elseif score|ge,70}}
Grade: C
{{elseif score|ge,60}}
Grade: D
{{else}}
Grade: F
{{endif}}
Note:
{{elseif}}and{{elif}}are interchangeable - use whichever you prefer.
Negation
Use ! to negate a condition:
{{if !user.email_verified}}
Please verify your email address.
{{endif}}
Loops
Basic Loop
Iterate over collections with for...in:
<ul>
{{for product in products}}
<li>{{:product.name}} - ${{:product.price}}</li>
{{endfor}}
</ul>
Pseudo-Variables
Access loop metadata using @@ prefix:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
@@index |
Current iteration (1-based) |
@@odd |
True for odd iterations (1, 3, 5…) |
@@even |
True for even iterations (2, 4, 6…) |
@@first |
True for the first iteration |
@@last |
True for the last iteration (requires known count) |
<table>
{{for item in items}}
<tr class="{{if item.@@odd}}odd-row{{else}}even-row{{endif}}{{if item.@@first}} first{{endif}}{{if item.@@last}} last{{endif}}">
<td>{{:item.@@index}}</td>
<td>{{:item.name}}</td>
</tr>
{{endfor}}
</table>
Note:
@@lastrequires the collection to have a known count. For TDataSet record iteration, this requires the dataset to be fully fetched (RecordCount must be available). For field iteration, object lists, and JSON arrays,@@lastworks automatically.
Continue Statement
Skip iterations conditionally:
{{for product in products}}
{{if product.is_hidden}}
{{continue}}
{{endif}}
<div>{{:product.name}}</div>
{{endfor}}
Nested Loops
{{for category in categories}}
<h2>{{:category.name}}</h2>
<ul>
{{for product in category.products}}
<li>{{:product.name}}</li>
{{endfor}}
</ul>
{{endfor}}
Empty Collections (For-Else)
Handle empty collections elegantly with {{else}} inside the loop (Jinja2-style):
{{for order in orders}}
Order #{{:order.id}}: ${{:order.total}}
{{else}}
No orders found.
{{endfor}}
The {{else}} block executes only when the collection is empty. This is cleaner than wrapping the loop in an {{if}} block.
Another example - search results:
{{for result in results}}
<div class="result">
<a href="{{:result.url}}">{{:result.title}}</a>
</div>
{{else}}
<p>No results found for "{{:query}}".</p>
{{endfor}}
Filters
Filters transform values using the pipe | syntax.
Basic Usage
{{customer.name|uppercase}}
{{:product.description|trunc,100}}
{{order.date|datetostr,"dd/mm/yyyy"}}
Chained Filters
Apply multiple filters in sequence:
{{:user.email|lowercase|default,"no-email@example.com"}}
{{:product.code|uppercase|lpad,10,"0"}}
Built-in Filters Reference
Text Transformation:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
uppercase |
Convert to uppercase | {{:name|uppercase}} |
lowercase |
Convert to lowercase | {{:email|lowercase}} |
capitalize |
Capitalize words | {{:title|capitalize}} |
trunc,n |
Truncate with ellipsis | {{:text|trunc,50}} |
Padding:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
lpad,n[,char] |
Left-pad to length | {{:id|lpad,6,"0"}} → 000042 |
rpad,n[,char] |
Right-pad to length | {{:code|rpad,10,"-"}} |
Date/Time:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
datetostr[,format] |
Format date | {{:date|datetostr,"yyyy-mm-dd"}} |
datetimetostr[,format] |
Format datetime | {{:timestamp|datetimetostr}} |
formatdatetime,format |
Custom format | {{:dt|formatdatetime,"dddd, mmmm d"}} |
ISO 8601 Default Format: The
datetostrfilter defaults toyyyy-mm-ddanddatetimetostrdefaults toyyyy-mm-dd hh:nn:ss. This ensures consistent, locale-independent output. To use a different format, specify it as a parameter:{{:date|datetostr,"dd/mm/yyyy"}}.ISO 8601 String Parsing: These filters also accept ISO 8601 date strings as input (e.g.,
2025-12-30T14:23:08.281+01:00,2025-12-30T14:23:08Z,2025-12-30). This is useful when working with JSON data or web APIs. Empty strings return empty output without errors.
Numeric:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
round,decimals |
Round number | {{:price|round,-2}} → 19.99 |
formatfloat,format |
Format number | {{:amount|formatfloat,"#,##0.00"}} |
mod,n |
Modulo operation | {{:num|mod,2}} |
Default & Comparison:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
default,value |
Fallback if empty/zero | {{:nickname|default,"Guest"}} |
eq,value |
Equal (for conditions) | {{if status|eq,"active"}} |
ne,value |
Not equal | {{if type|ne,"admin"}} |
gt,value |
Greater than | {{if age|gt,17}} |
ge,value |
Greater or equal | {{if score|ge,60}} |
lt,value |
Less than | {{if stock|lt,10}} |
le,value |
Less or equal | {{if items|le,5}} |
contains,text |
Contains substring | {{if name|contains,"Jr"}} |
icontains,text |
Contains (case-insensitive) | {{if email|icontains,"gmail"}} |
Utility:
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
totrue |
Always returns true | {{if var|totrue}} |
tofalse |
Always returns false | {{if var|tofalse}} |
urlencode |
URL-encode a string | {{:query|urlencode}} |
truncate,n[,ellipsis] |
Truncate to n chars with ellipsis | {{:text|truncate,50}} |
json |
Serialize object to JSON | {{:obj|json}} |
Functions (applied to empty value):
| Filter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
version |
TemplatePro version | {{:|version}} |
Custom Filters
Register custom transformation functions:
// Define the filter function
function CurrencyFilter(const Value: TValue;
const Params: TArray<TFilterParameter>): TValue;
begin
Result := Format('$%.2f', [Value.AsExtended]);
end;
// Register after compilation
Template.AddFilter('currency', CurrencyFilter);
Template usage:
Price: {{:product.price|currency}}
Filter with parameters:
function RepeatFilter(const Value: TValue;
const Params: TArray<TFilterParameter>): TValue;
var
i, Count: Integer;
S: string;
begin
Count := Params[0].ParIntValue;
S := '';
for i := 1 to Count do
S := S + Value.AsString;
Result := S;
end;
Template.AddFilter('repeat', RepeatFilter);
Usage:
{{:"-"|repeat,20}} outputs: --------------------
Macros
Macros are reusable template fragments with parameters.
Definition
{{macro alert(message, type)}}
<div class="alert alert-{{:type}}">
{{:message}}
</div>
{{endmacro}}
Calling Macros
Use the {{>}} syntax to invoke macros:
{{>alert("Operation successful!", "success")}}
{{>alert("Please check your input.", "warning")}}
{{>alert("An error occurred.", "error")}}
Macros Without Parameters
{{macro divider()}}
<hr class="section-divider">
{{endmacro}}
{{>divider()}}
Macros with Variables
Pass template variables as arguments:
{{macro user_card(user)}}
<div class="user-card">
<h3>{{:user.name}}</h3>
<p>{{:user.email}}</p>
</div>
{{endmacro}}
{{for u in users}}
{{>user_card(u)}}
{{endfor}}
Nested Macros
Macros can call other macros:
{{macro icon(name)}}
<i class="icon icon-{{:name}}"></i>
{{endmacro}}
{{macro button(text, icon_name)}}
<button class="btn">
{{>icon(icon_name)}} {{:text}}
</button>
{{endmacro}}
{{>button("Save", "check")}}
{{>button("Delete", "trash")}}
Template Composition
Include
Include external template files:
{{include "partials/header.tpro"}}
<main>
<h1>{{:page_title}}</h1>
{{:content}}
</main>
{{include "partials/footer.tpro"}}
Include with Variable Mappings
Pass variables to included templates:
{{include "components/product_card.tpro", product = :item, show_price = true}}
product_card.tpro:
<div class="product-card">
<h3>{{:product.name}}</h3>
{{if show_price}}
<p class="price">${{:product.price}}</p>
{{endif}}
</div>
You can pass different types:
{{include "alert.tpro", message = "Success!", type = "success"}}
{{include "alert.tpro", message = :error_message, type = "error"}}
{{include "counter.tpro", count = @(items_count * 2)}}
Dynamic Include
Include templates based on variables:
{{include :template_name}}
Template Inheritance
Create a base layout with replaceable blocks:
base.tpro:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>{{block "title"}}My Site{{endblock}}</title>
</head>
<body>
<nav>{{block "navigation"}}Default nav{{endblock}}</nav>
<main>
{{block "content"}}{{endblock}}
</main>
<footer>{{block "footer"}}Copyright 2025{{endblock}}</footer>
</body>
</html>
page.tpro:
{{extends "base.tpro"}}
{{block "title"}}{{:page_title}} - My Site{{endblock}}
{{block "content"}}
<h1>{{:page_title}}</h1>
<p>{{:content}}</p>
{{endblock}}
Inheritance rules:
- Child templates can only extend one parent
- Blocks not defined in the child use the parent’s content
- Content outside blocks in child templates is ignored
The inherited Keyword
Use {{inherited}} to include parent block content while adding your own:
base.tpro:
<head>
{{block "head"}}
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My Site</title>
{{endblock}}
</head>
page.tpro:
{{extends "base.tpro"}}
{{block "head"}}
{{inherited}}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="page.css">
<script src="page.js"></script>
{{endblock}}
Output:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My Site</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="page.css">
<script src="page.js"></script>
</head>
Multi-level Inheritance
Templates can extend other templates that themselves extend other templates, creating unlimited inheritance chains:
level1_base.tpro:
<html>
{{block "content"}}Base Content{{endblock}}
</html>
level2_section.tpro:
{{extends "level1_base.tpro"}}
{{block "content"}}Section: {{inherited}}{{endblock}}
level3_page.tpro:
{{extends "level2_section.tpro"}}
{{block "content"}}Page -> {{inherited}}{{endblock}}
Output:
<html>
Page -> Section: Base Content
</html>
Multi-level inheritance features:
{{inherited}}includes content from the immediate parent at each level- Circular inheritance is detected and raises a clear error
- Self-inheritance (a template extending itself) is also detected
- Works correctly with partial block overrides at any level
Working with Datasets
TemplatePro integrates seamlessly with Delphi TDataSet components, providing both record iteration and field metadata access for dynamic UI generation.
Iterating Records
<table>
<tr><th>Code</th><th>Name</th><th>Price</th></tr>
{{for product in products}}
<tr>
<td>{{:product.Code}}</td>
<td>{{:product.Name}}</td>
<td>{{:product.Price|formatfloat,"0.00"}}</td>
</tr>
{{endfor}}
</table>
Delphi code:
Template.SetData('products', ProductsDataSet);
Field Metadata Iteration
TemplatePro can iterate over dataset field definitions using the .fields suffix. This enables automatic form generation, dynamic table headers, and metadata-driven UIs.
Syntax: {{for field in dataset.fields}}...{{endfor}}
Field Properties Reference
When iterating fields, each field object exposes these properties:
| Property | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
FieldName |
String | Internal field name (database column) | CUSTOMER_ID |
DisplayLabel |
String | User-friendly label for UI | Customer ID |
DisplayName |
String | Display name | Customer ID |
DataType |
String | Field data type | ftString, ftInteger, ftDate |
Size |
Integer | Field size (for strings) | 50 |
Index |
Integer | Field index (0-based) | 0, 1, 2 |
Required |
Boolean | Field is required (NOT NULL) | true/false |
ReadOnly |
Boolean | Field is read-only | true/false |
Visible |
Boolean | Field is visible | true/false |
IsNull |
Boolean | Current value is NULL | true/false |
AsString |
String | Current value as string | "John" |
| (no property) | String | {{:field}} returns current value |
"John" |
Complete Example: Automatic HTML Form Generation
This example generates a complete HTML form from dataset metadata, with proper input types, validation attributes, and Bootstrap styling:
{{# Automatic Form Generator - uses dataset field metadata #}}
<form method="post" action="/save" class="needs-validation" novalidate>
<h2>Edit {{:formtitle}}</h2>
{{for f in customers.fields}}
{{if f.Visible}}
<div class="mb-3">
{{# Label with required indicator #}}
<label for="{{:f.FieldName}}" class="form-label">
{{:f.DisplayLabel}}{{if f.Required}} <span class="text-danger">*</span>{{endif}}
</label>
{{# Input type based on DataType #}}
{{if f.DataType|eq,"ftInteger"}}
<input type="number"
class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="{{:f}}"
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftFloat"}}
<input type="number"
step="0.01"
class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="{{:f}}"
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftDate"}}
<input type="date"
class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="{{:f|datetostr,"yyyy-mm-dd"}}"
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftDateTime"}}
<input type="datetime-local"
class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="{{:f|datetimetostr,"yyyy-mm-ddThh:nn"}}"
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftBoolean"}}
<div class="form-check">
<input type="checkbox"
class="form-check-input"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="1"
{{if f}}checked{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}disabled{{endif}}>
<label class="form-check-label" for="{{:f.FieldName}}">{{:f.DisplayLabel}}</label>
</div>
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftMemo"}}
<textarea class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
rows="4"
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>{{:f}}</textarea>
{{else}}
{{# Default: text input with maxlength from Size #}}
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="{{:f.FieldName}}"
name="{{:f.FieldName}}"
value="{{:f}}"
{{if f.Size|gt,0}}maxlength="{{:f.Size}}"{{endif}}
{{if f.Required}}required{{endif}}
{{if f.ReadOnly}}readonly{{endif}}>
{{endif}}
{{# Help text showing field constraints #}}
{{if f.Size|gt,0}}
<div class="form-text">Max {{:f.Size}} characters</div>
{{endif}}
</div>
{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
<div class="mt-4">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Save</button>
<a href="/list" class="btn btn-secondary">Cancel</a>
</div>
</form>
Delphi code to use this template:
var
Template: ITProCompiledTemplate;
begin
// Load and compile template
Template := TTProCompiler.CreateFromFile('customer_form.tpro');
// Pass the dataset - TemplatePro reads both data and metadata
Template.SetData('customers', CustomersDataSet);
Template.SetData('formtitle', 'Customer');
// Render the form
Result := Template.Render;
end;
Dynamic Table with Field Headers
Generate a complete data table with headers from field metadata:
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
{{for f in data.fields}}
{{if f.Visible}}
<th>{{:f.DisplayLabel}}</th>
{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{{for row in data}}
<tr>
{{for f in data.fields}}
{{if f.Visible}}
<td>
{{if f.DataType|eq,"ftDate"}}
{{:row[f.FieldName]|datetostr}}
{{elseif f.DataType|eq,"ftFloat"}}
{{:row[f.FieldName]|formatfloat,"#,##0.00"}}
{{else}}
{{:row[f.FieldName]}}
{{endif}}
</td>
{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
</tr>
{{else}}
<tr><td colspan="100">No records found.</td></tr>
{{endfor}}
</tbody>
</table>
Expression Conditions with Fields
Use expressions to check field properties:
{{for f in customers.fields}}
{{if @(f.Index = 0)}}
<th>{{:f.DisplayLabel}}</th> {{# First field as header #}}
{{else}}
<td>{{:f}}</td>
{{endif}}
{{endfor}}
Field Iteration Pseudo-Variables
Field loops support the same pseudo-variables as regular loops:
{{for f in data.fields}}
{{:f.@@index}}. {{:f.FieldName}}
{{if f.@@first}}(first){{endif}}
{{if f.@@last}}(last){{endif}}
{{endfor}}
Output Configuration
Line Endings
TemplatePro provides cross-platform control over output line endings.
Input: Templates with any line ending style (CRLF, LF, CR) are automatically recognized.
Output: Configure the output line ending style:
Template.OutputLineEnding := lesLF; // Unix-style (default)
Template.OutputLineEnding := lesCRLF; // Windows-style
Template.OutputLineEnding := lesCR; // Classic Mac
Template.OutputLineEnding := lesNative; // Platform default
Available values:
| Value | Description | Characters |
|---|---|---|
lesLF |
Unix/Linux/Modern Mac | #10 |
lesCRLF |
Windows | #13#10 |
lesCR |
Classic Mac | #13 |
lesNative |
Current platform default | varies |
Tip: Use
lesLF(the default) for maximum portability. Most modern systems handle LF correctly.
API Reference
TTProCompiler
The template compiler.
var
Compiler: TTProCompiler;
begin
Compiler := TTProCompiler.Create;
try
// Compile from string
Template := Compiler.Compile(TemplateString);
// Compile from string with file path reference (for includes)
Template := Compiler.Compile(TemplateString, 'templates/page.tpro');
finally
Compiler.Free;
end;
end;
Static methods:
// Compile and render in one call
Output := TTProCompiler.CompileAndRender(
'Hello {{:name}}!',
['name'],
['World']
);
ITProCompiledTemplate
The compiled template interface.
Setting data:
Template.SetData('name', 'John'); // String
Template.SetData('age', 30); // Integer
Template.SetData('price', 19.99); // Float
Template.SetData('is_active', True); // Boolean
Template.SetData('user', UserObject); // Object
Template.SetData('items', ItemsList); // TObjectList
Template.SetData('customers', CustomersDataSet); // TDataSet
Adding filters:
Template.AddFilter('myfilter', MyFilterFunction);
Template.AddFilter('myfilter',
function(const Value: TValue; const Params: TArray<TFilterParameter>): TValue
begin
Result := '[' + Value.AsString + ']';
end
);
Rendering:
Output := Template.Render;
Persistence:
Template.SaveToFile('template.tpc');
Template := TTProCompiledTemplate.CreateFromFile('template.tpc');
Properties:
Template.OutputLineEnding := lesLF;
Template.FormatSettings := @MyFormatSettings;
Exceptions
try
Template := Compiler.Compile(TemplateString);
Output := Template.Render;
except
on E: ETProCompilerException do
// Syntax errors, missing end tags, invalid directives
ShowMessage('Compilation error: ' + E.Message);
on E: ETProRenderException do
// Runtime errors: missing variables, type mismatches
ShowMessage('Render error: ' + E.Message);
on E: ETProException do
// General TemplatePro errors
ShowMessage('Template error: ' + E.Message);
end;
Best Practices
Template Organization
templates/
layouts/
base.tpro
admin.tpro
partials/
header.tpro
footer.tpro
navigation.tpro
components/
alert.tpro
card.tpro
form_field.tpro
pages/
home.tpro
products.tpro
checkout.tpro
emails/
order_confirmation.tpro
password_reset.tpro
Performance Tips
- Compile once, render many: Keep compiled templates for reuse.
- Use pre-compiled templates: Save
.tpcfiles for production. - Avoid complex logic in templates: Pre-process data in Delphi.
- Use appropriate data structures: TObjectList over arrays for large collections.
Security
- Escape user input: Be cautious with user-provided data in templates.
- Validate include paths: Don’t allow user-controlled template paths.
- Limit template complexity: Set reasonable limits on nesting depth.
Debugging
// Dump compiled tokens for debugging
Template.DumpToFile('debug_output.txt');
// Use the OnGetValue event for custom variable resolution
Template.OnGetValue := procedure(const DataSource, Members: string;
var Value: TValue; var Handled: Boolean)
begin
WriteLn('Accessing: ', DataSource, '.', Members);
end;
Autoescape Block
Control HTML encoding for a section of the template.
Default Behavior: HTML Encoding is ON
By default, all variable output is HTML-encoded for security (XSS prevention). Special characters like <, >, &, " are converted to HTML entities.
{{:myhtml}}
If myhtml contains <div>Hello</div>, output will be: <div>Hello</div>
Disabling Autoescape for a Block
Use {{autoescape false}} to output raw HTML for trusted content:
{{autoescape false}}
{{:trusted_html}}
{{endautoescape}}
Explicit Raw Output with $ Suffix
For a single variable, use the $ suffix to skip HTML encoding:
Encoded (default): {{:myhtml}}
Raw (explicit): {{:myhtml$}}
This is useful when you need raw output for just one variable without changing the autoescape mode.
Complete Example
** Autoescape Demo **
Default (encoded): {{:myhtml}}
{{autoescape false}}
Autoescape off: {{:myhtml}}
{{endautoescape}}
Back to default: {{:myhtml}}
Explicit raw: {{:myhtml$}}
With myhtml = "<b>Bold</b>":
** Autoescape Demo **
Default (encoded): <b>Bold</b>
Autoescape off: <b>Bold</b>
Back to default: <b>Bold</b>
Explicit raw: <b>Bold</b>
Security Note: Only disable autoescape or use
$suffix for trusted content. User-provided data should always be encoded to prevent XSS attacks.
Raw Blocks
Output template syntax literally without parsing using {{raw}}...{{endraw}}.
Basic Usage
Normal output: {{:value1}}
{{raw}}
This is literal: {{:value1}} {{for x in items}}{{endfor}}
{{endraw}}
Back to normal: {{:value1}}
Output:
Normal output: true
This is literal: {{:value1}} {{for x in items}}{{endfor}}
Back to normal: true
Use Cases
- Documenting TemplatePro syntax in templates
- Outputting JavaScript template literals that use similar syntax
- Embedding code examples in generated documentation
Whitespace Control
Control whitespace around template tags using - modifiers.
Syntax
| Modifier | Effect |
|---|---|
{{- ... }} |
Strip whitespace before the tag |
{{ ... -}} |
Strip whitespace after the tag |
{{- ... -}} |
Strip whitespace on both sides |
Examples
Before{{- :value -}}After
Output: BeforetrueAfter (no spaces)
Left strip: {{- :value}}END
Output: Left strip:trueEND (spaces before tag removed)
Right strip:{{:value -}} END
Output: Right strip:trueEND (spaces after tag removed)
Use in Loops
Whitespace control is especially useful in loops to avoid unwanted blank lines:
<ul>
{{- for item in items -}}
<li>{{:item.name}}</li>
{{- endfor -}}
</ul>
Comments
Add comments that won’t appear in output:
{{# This is a single-line comment #}}
{{#
This is a multi-line comment.
It can span several lines.
#}}
Flow Control
Exit Statement
Stop rendering the template:
{{if critical_error}}
<p>A critical error occurred.</p>
{{exit}}
{{endif}}
{{# This content won't render if there's an error #}}
<p>Normal content here.</p>
Migration Notes
From Version 1.0 to 1.1
Version 1.1 is a bugfix release with no breaking changes:
- Nullable types with filters: Nullable types (e.g.,
NullableString,NullableInt32) now work correctly with all filters. Previously,{{:nullableVar|uppercase}}displayed(record)instead of the actual value. - Null-safe filters: Applying string filters (
uppercase,lowercase,capitalize,urlencode) to null Nullable values no longer causesEInvalidCastexceptions. Null values safely produce an empty string. - TField null handling: Null
TFieldvalues are now handled correctly across all filters (default,datetostr,datetimetostr,round,formatfloat, etc.). - Memory leak fix: Fixed a memory leak caused by the
IExprEvaluatorinterface reference counting interacting with anonymous method closures.
From Version 0.8.x
Set syntax change:
{{# Old syntax (0.8.x) #}}
{{set myvar = 42}}
{{# New syntax (1.0) #}}
{{set myvar := 42}}
And/Or filters removed:
{{# Old syntax (deprecated) #}}
{{if value1|and,value2}}
{{# New syntax #}}
{{if @(value1 and value2)}}
Features in 1.0:
{{inherited}}keyword for including parent block content- Multi-level template inheritance (A extends B extends C)
- Circular inheritance detection
{{elseif}}/{{elif}}conditional branches- Date filters default to ISO 8601 format (
yyyy-mm-dd/yyyy-mm-dd hh:nn:ss) - Date filters accept ISO 8601 strings from JSON/APIs
{{autoescape true/false}}...{{endautoescape}}for HTML encoding control{{raw}}...{{endraw}}for literal output without parsing- Whitespace control with
{{-and-}}modifiers - New filters:
urlencode,truncate,json
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between TemplatePro and other Delphi template engines?
TemplatePro offers a Jinja2/Smarty-inspired syntax that is familiar to web developers, while being specifically optimized for Delphi. Unlike simpler string replacement engines, TemplatePro supports:
- Full expression evaluation
- Template inheritance
- Macros with parameters
- Native TDataSet support
- Compiled template caching
Can I use TemplatePro with DMVCFramework?
Yes! TemplatePro is the default template engine for DMVCFramework. It integrates seamlessly for server-side HTML rendering in web applications.
Is TemplatePro thread-safe?
Yes. Compiled templates (ITProCompiledTemplate) are thread-safe for rendering. You can compile once and render from multiple threads simultaneously.
What data types can I pass to templates?
TemplatePro supports:
- Simple types (string, integer, float, boolean)
- Objects with published properties
TObjectList<T>and other generic listsTDataSetand descendants- JSON objects (
TJDOJsonObject) - Nullable types from
MVCFramework.Nullables
How do I handle HTML escaping?
By default, all variable output IS HTML-encoded for security (XSS prevention). Characters like <, >, &, " are automatically converted to HTML entities.
To output raw HTML for trusted content only, use:
{{:trusted_html$}} {{# $ suffix = raw output #}}
{{autoescape false}}
{{:trusted_block}} {{# block with autoescape off #}}
{{endautoescape}}
Security: Never disable autoescape for user-provided data.
Can I extend TemplatePro with custom filters?
Yes! Register custom filters using TTProConfiguration.OnContextConfiguration:
TTProConfiguration.OnContextConfiguration :=
procedure(const Template: ITProCompiledTemplate)
begin
Template.AddTemplateFunction('myfilter', MyFilterFunction);
end;
What’s the performance like?
TemplatePro compiles templates to an internal token representation. Rendering is very fast:
- Compilation: ~1ms for typical templates
- Rendering: ~0.1ms for simple templates, scales linearly with complexity
- Memory: Minimal footprint, compiled templates are lightweight
Does TemplatePro support internationalization (i18n)?
TemplatePro provides locale-aware formatting through FormatSettings. For full i18n, combine with your localization framework and pass translated strings as variables.
Links
TemplatePro Version 1.1 - Updated January 2026
Comments
comments powered by Disqus